Participles are descriptive terms that are derived from verbs and indicate a relationship with them. Participles can function as nouns or adjectives. There are two types of participles in Arabic: active participles and passive participles.
Active Participles in Arabic
An active participle describes the doer of an action. The active participle is derived from the corresponding verb. The basic and most common form of an active participle is فــاعِــل (fā‘il).
For instance, from the verb كَـتَـبَ (kataba) ‘he wrote,’ we can derive the active participle كـاتِـب (kātib) ‘writer.’
Note that the active participle can vary by gender and number. Feminine and plural markers can be added to the basic active participle form as follows:
| Masculine | Feminine | |
| Singular | فــاعِــل fā‘il | فــاعِــلَـة fā‘ilah |
| Plural (nominative) | فــاعِــلـون fā‘ilūn | فــاعِــلات fā‘ilāt |
Think of the English suffix “-er” in “writer,” “-or” in “inspector,” “-ist” in “novelist,” “-ian” in “historian,” or “-ent” in “correspondent.” Similarly, Arabic uses a variety of prefixes, infixes, and suffixes to form the active participle.
The most common patterns of the active participle in Arabic are:
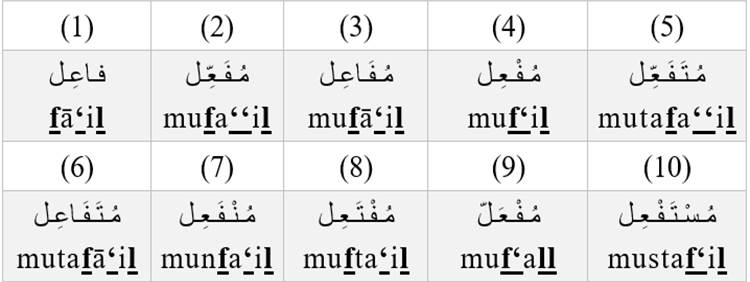
Some common words have active participle forms, but have historically acquired their own specific meanings, such as جـاهِـز (jāhiz) ‘ready,’ شـارِع (shāri‘) ‘street,’ and راهِـب (rāhib) ‘monk.’
Here are some examples of the different active participle patterns:
| Verb | Pattern | Active Participle |
| ذَهَـبَ (dhahaba) he went | (1) | ذاهِـب (dhāhib) goer/going |
| جَـلَـسَ (jalasa) he sat | (1) | جـالِـس (jālis) sitting |
| قَـتَـلَ (qatala) he killed | (1) | قـاتِـل (qātil) killer |
| عَـلَّـمَ (‘allama) he taught | (2) | مُـعَـلِّـم (mu‘allim) teacher |
| فَـتَّـشَ (fattasha) he inspected | (2) | مُـفَـتِّـش (mufattish) inspector |
| قـاتَـلَ (qātala) he fought | (3) | مُـقـاتِـل (muqātil) fighter |
| سـاعَـدَ (sā‘ada) he helped | (3) | مُـسـاعِـد (musā‘id) helper |
| قـاوَمَ (qāwama) he resisted | (3) | مُـقـاوِم (muqāwim) resistant |
| أَسْـلَـمَ (’aslama) he submitted | (4) | مُـسْـلِـم (muslim) Muslim |
| أَسْـعَــفَ (’as‘afa) he aided | (4) | مُـسْـعِـف (mus‘if) paramedic |
| تَـحَـدَّثَ (taḥaddatha) he talked | (5) | مُـتَحَدِّث (mutaḥaddith) spokesman |
| تَخَصَّصَ (takhaṣṣaṣa) he specialized | (5) | مُتَخَصِّص (mutakhaṣṣiṣ) specialist |
| تَـقـاعَـدَ (taqā‘ada) he retired | (6) | مُـتَـقـاعِـد (mutaqā‘id) retired |
| تَـعـاوَنَ (ta‘āwana) he cooperated | (6) | مُـتَـعاوِن (muta‘āwin) cooperative |
| اِنْـكَـمَـشَ (inkamasha) it shrank | (7) | مُنْـكَـمِـش (munkamish) shrunk |
| اِنْـفَـجَـرَ (infajara) it exploded | (7) | مُـنْـفَـجِـر (munfajir) exploding |
| اِعْـتَـرَضَ (i‘taraḍa) he objected | (8) | مُعْـتَـرِض (mu‘tariḍ) objecting |
| اِسْـتَـمَـعَ (istama‘a) he listened | (8) | مُسْـتَـمِـع (mustami‘) listener |
| اِحْـمَـرَّ (iḥmarra) it became red | (9) | مُحْـمَـرّ (muḥmarr) reddish |
| اِسْوَدَّ (iswadda) it became black | (9) | مُـسْـوَدّ (muswadd) blackish |
| اِسْـتَـثْـمَرَ (istathmara) he invested | (10) | مُسْـتَـثْـمِـر (mustathmir) investor |
| اِسْـتَـأْجَـرَ (ista’jara) he rented | (10) | مُسْـتَـأْجِـر (musta’jir) tenant |
Passive Participles in Arabic
A passive participle describes the action performed or the object upon which the action is done. The passive participle is derived from the corresponding verb. The basic and most common form of a passive participle is مَـفْـعـول (maf‘ūl).
For instance, from the verb كَـتَـبَ (kataba) ‘he wrote,’ we can derive the passive participle مَـكْـتـوب (maktūb), meaning ‘written’ or ‘letter.’
Feminine and plural markers can be added to the basic passive participle form as follows:
| Masculine | Feminine | |
| Singular | مَـفْـعـول maf‘ūl | مَـفْـعـولَـة maf‘ūlah |
| Plural (nominative) | مَـفْـعـولـون maf‘ūlūn | مَـفْـعـولات maf‘ūlāt |
Other common patterns of the passive participle are:
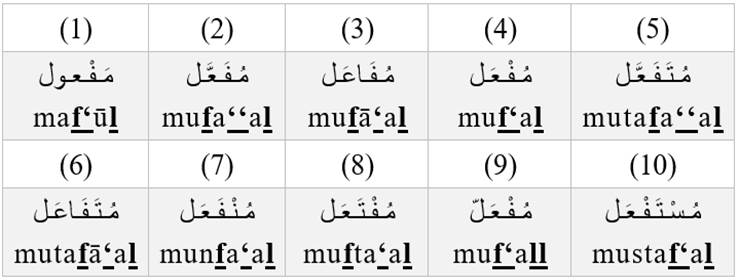
Some common words have a passive participle form, but have historically acquired their own specific meanings, such as مَـكْـتـوب (maktūb) ‘letter’ and مَـشْـروع (mashrū‘) ‘project.’
Think of the English suffix “-ed” in “booked,” “-en” in “written,” or “-ne” in “done.” Similarly, Arabic uses a variety of prefixes, infixes, and suffixes to form the passive participle.
Here are examples of the most common patterns of the passive participle in Arabic:
| Verb | Pattern | Active Participle |
| فَــهِــمَ (fahima) he understood | (1) | مَــفْـهــوم (mafhūm) concept |
| حَـجَـزَ (ḥajaza) he reserved | (1) | مَـحْـجـوز (maḥjūz) reserved |
| قَـتَـلَ (qatala) he killed | (1) | مَـقْـتـول (maqtūl) killed |
| عَـقَّـدَ (‘aqqada) he complicated | (2) | مُـعَـقَّـد (mu‘aqqad) complicated |
| وَظَّـفَ (waẓẓafa) he employed | (2) | مُـوَظَّـف (muwaẓẓaf) employee |
| عـاقَـبَ (‘āqaba) he punished | (3) | مُـعـاقَـب (mu‘āqab) punished |
| بـارَكَ (bāraka) he blessed | (3) | مُـبـارَك (mubārak) blessed |
| أَفْـرَدَ (’afrada) he singled out | (4) | مُـفْـرَد (mufrad) singular |
| أَعْـجَـبَ (’a‘jaba) he impressed | (4) | مُـعْـجَـب (mu‘jab) impressed |
| تَـخَـيَّـلَ (takhayyala) he imagined | (5) | مُـتَـخَـيَّـل (mutakhayyal) imagined |
| تَـوَقَّـعَ (tawaqqa‘a) he expected | (5) | مُـتَـوَقَّـع (mutawaqqa‘) expected |
| تَـقـاسَـمَ (taqāsama) he shared | (6) | مُـتَـقـاسَـم (mutaqāsam) shared |
| تَـبـادَلَ (tabādala) he exchanged | (6) | مُـتَـبـادَل (mutabādal) mutual |
| اِنْـطَـلَـقَ (inṭalaqa) he set off | (7) | مُـنْـطَـلَق (munṭalaq) starting point |
| اِنْـحَـدَرَ (inḥadara) he declined | (7) | مُـنْـحَـدَر (munḥadar) slope |
| اِنْـتَـخَـبَ (intakhaba) he elected | (8) | مُـنْـتَـخَـب (muntakhab) elected |
| اِجْـتَـمَـعَ (ijtama‘a) he gathered | (8) | مُجْـتَـمَـع (mujtama‘) society |
| اِحْـمَـرَّ (iḥmarra) it became red | (9) | مُحْـمَـرّ (muḥmarr) reddish |
| اِسْوَدَّ (iswadda) it became black | (9) | مُـسْـوَدّ (muswadd) blackish |
| اِسْـتَـقْـبَـلَ (istaqbala) he received | (10) | مُـسْـتَـقْـبَـل (mustaqbal) future |
| اِسْـتَـأْجَـرَ (ista’jara) he rented | (10) | مُسْـتَـأْجَـر (musta’jar) rented |
Notice that Pattern (9) of the passive participle is identical to that of the active participle. This pattern is rarely used, except for a few color adjectives.
Other lessons in Level IV:









