In this lesson, we cover adjectives in Arabic. Adjectives in Arabic agree in gender, number, and grammatical case with the noun they describe.
Table of Contents
- Adjective Patterns in Arabic
- Participles as Adjectives in Arabic
- Relative Adjectives in Arabic
- Diminutives
- Level III – Intermediate I (B1)
Adjective Patterns in Arabic
The most common adjective patterns in Arabic are:
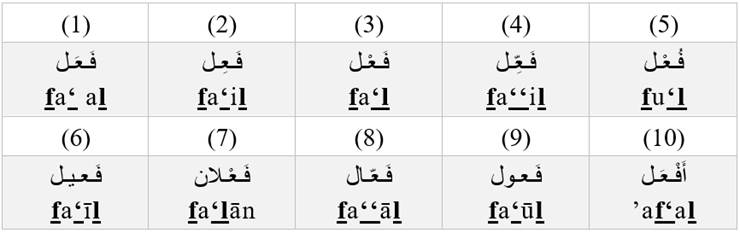
Here are some examples that follow the different adjective patterns outlined above:
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) |
| حَـسَـن ḥasan good | خَـشِـن khashin rough | سَـهْـل sahl easy | جَـيِّـد jayyid good | حُـرّ ḥurr free |
| وَسَـط wasaṭ middle | مَـرِن marin flexible | ضَـخْـم ḍakhm huge | سَـيِّء sayyi’ bad | مُـرّ murr bitter |
| (6) | (7) | (8) | (9) | (10) |
| قَـصـيـر qaṣīr short | نَـعْـسـان na‘sān sleepy | فَـعّـال fa‘‘āl effective | كَـسـول kasūl lazy | أَسْـــوَد ’aswad black |
| صَـغـيـر ṣaghīr small | عَـطْـشـان ‘aṭ shān thirsty | جَــذّاب jadhdhāb attractive | حَـسـود ḥasūd envious | أَخْـضَـر ’akh ḍar green |
Note that the feminine forms of the patterns فَـعْـلان (fa‘lān) and أَفْـعَـل (’af‘al) often follow the patterns فَـعْـلى (fa‘lā) and فَـعْـلاء (fa‘lā’), respectively.
Participles as Adjectives in Arabic
In addition to the above ten patterns, we will learn in Level IV, Lesson 7 about active and passive participles, which can also function as adjectives. The most common pattern of an active participle is فــاعِــل (fā‘il). For instance, from the verb لَـمَـعَ (lama‘a) ‘he/it shone,’ we derive the active participle لامِـع (lāmi‘) ‘shining.’
Similarly, the most common pattern of a passive participle is مَـفْـعـول (maf‘ūl). For example, from the verb كَـتَـبَ (kataba) ‘he wrote,’ we derive the passive participle مَـكْـتـوب (maktūb) ‘written.’
Relative Adjectives in Arabic
Relative adjectives in Arabic are formed by adding the masculine suffix ـيّ (-iyy) or the feminine suffix ـيَّـة (-iyyah) to the noun. This is similar to the use of the suffix “-al” in “central,” “-ic” in “Islamic,” or “-i” in “Iraqi” in English.
Here are some examples of relative adjectives:
| Noun | Relative Adjective (m) | Relative Adjective (f) |
| شَـمْـس shams sun | شَـمْـسِـيّ shamsiyy solar (m) | شَـمْـسِـيَّـة shamsiyyah solar (f) |
| تـاريـخ tārīkh history | تـاريـخـيّ tārīkhiyy historical (m) | تـاريـخـيَّـة tārīkhiyyah historical (f) |
| شَـهْـر shahr month | شَـهْـرِيّ shahriyy monthly (m) | شَـهْـرِيَّـة shahriyyah monthly (f) |
| ذَهَـب dhahab gold | ذَهَـبِـيّ dhahabiyy golden (m) | ذَهَـبِـيَّـة dhahabiyyah golden (f) |
If the noun ends with a ة (tā’ marbūṭah) ‘tied-t,’ it is dropped after adding the suffix ـيّ (-iyy) or ـيَّـة (-iyyah). For example:
| Noun | Relative Adjective (m) | Relative Adjective (f) |
| سِـيـاسَـة siyāsah policy, politics | سِـيـاسِـيّ siyāsiyy political, politician (m) | سِـيـاسِـيَّـة siyāsiyyah political, politician (f) |
| ثَـقـافَـة thaqāfah culture | ثَـقـافِـيّ thaqāfiyy cultural (m) | ثَـقـافِـيَّـة thaqāfiyyah cultural (f) |
The suffixes ـيّ (-iyy) and ـيَّـة (-iyyah) are often used with nationalities. For example:
| Country | Nationality (m) | Nationality (f) |
| الْـجَـزائِـر al-jazā’ir Algeria | جَـزائِـرِيّ jazā’iriyy Algerian (m) | جَـزائِـرِيَّـة jazā’iriyyah Algerian (f) |
| مِـصْـر miṣr Egypt | مِـصْـرِيّ miṣriyy Egyptian (m) | مِـصْـرِيَّـة miṣriyyah Egyptian (f) |
| لُـبْنـان lubnān Lebanon | لُـبْنـانِـيّ lubnāniyy Lebanese (m) | لُـبْنـانِـيَّـة lubnāniyyah Lebanese (f) |
| الْـيَـمَـن al-yaman Yemen | يَـمَـنِـيّ yamaniyy Yemeni (m) | يَـمَـنِـيَّـة yamaniyyah Yemeni (f) |
In daily speech, an adjective ending with the masculine suffix ـيّ (-iyy) is pronounced ـي (-ī) in most spoken dialects, e.g., جَـزائِـري (jazā’irī) ‘Algerian,’ ذَهَـبـي (dhahabī) ‘golden,’ etc.
Diminutives
In the English language, we sometimes form the diminutive by suffixing “-ie” or “-y,” as in “doggie” for “dog” and “kitty” for “kitten,” indicating small size and sometimes the state or quality of being familiarly known, lovable, pitiable, or contemptible. Sometimes other suffixes are used, such as “-ette” in “kitchenette” and “novelette,” “-let” in “booklet” and “droplet,” and “-ling” in “duckling.”
In Arabic, diminutives are less common, especially in daily spoken language.
The general pattern of the diminutive in Arabic is فُـعَـيْـل (fu‘ayl) for masculine and فُـعَـيْـلَـة (fu‘aylah) for feminine nouns.
Here are some examples:
| بَـحْـر baḥr sea | بُـحَـيْـرَة buḥayrah lake |
| دَوْلَـة dawlah state | دُوَيْـلَـة duwaylah small state (pejorative) |
| كَـلْـب kalb dog | كُـلَـيْـب kulayb small dog |
The pattern فُـعَـيِّـل (fu‘ayyil) for masculine or فُـعَـيِّـلَـة (fu‘ayyilah) for feminine is used when the second radical is followed by a long vowel. For example, the diminutive of كِـتـاب (kitāb) ‘book’ is كُـتَـيِّـب (kutayyib) ‘booklet.’
Other lessons in Level III:









